In a competitive market where performance, security, and speed are paramount, adhering to robust software development best practices is no longer optional, it's the foundation of success. From startups to enterprises, the principles governing how we write, test, and deploy code directly impact user trust, team efficiency, and a product's longevity. Poor practices lead to technical debt, which, according to a 2023 report by Stepsize, consumes up to 42% of a developer's time, hindering innovation and growth. To truly succeed in modern software development, it is essential to focus on unlocking effective software engineering best practices that drive sustainable results.
Key Facts: Software Development in 2026
- 42% of developer time is consumed by managing technical debt rather than building new features (Stepsize Developer Survey, 2023)
- $2.41 trillion. Estimated annual cost of poor software quality in the U.S. alone (Consortium for Information & Software Quality, 2024)
- Teams practicing CI/CD deploy 208x more frequently than low-performing teams with 2,604x faster recovery from failures (DORA/Google State of DevOps Report)
- 60-70% of software defects originate in the design and requirements phase, not during coding, making upfront process investment critical (IBM Systems Sciences Institute)
This guide cuts through the noise to provide a curated roundup of 10 essential practices that high-performing teams use to build reliable, scalable, and maintainable software. We will move beyond generic advice to deliver specific, actionable insights you can implement immediately.
You will learn how to:
- Streamline collaboration with optimized Git workflows and code reviews.
- Build resilience through Test-Driven Development (TDD) and robust CI/CD pipelines.
- Design for scale using microservices and well-documented APIs.
- Embed security and performance from the start, not as an afterthought.
Each practice is broken down with actionable steps, real-world examples, and common pitfalls to avoid, ensuring you can implement these strategies effectively. Whether you're refining workflows for a daily newsletter or building a complex AI platform, mastering these fundamentals will future-proof your development lifecycle. Let's dive into the core strategies that separate great software from the rest.
Software Development Maturity Assessment
Rate your team on each practice (1 = Not implemented, 5 = Fully mature). Total score indicates your development maturity level:
| Practice | Score (1-5) | Signs of Maturity (Score 5) |
|---|---|---|
| Version Control | __ | Branch protection, conventional commits, no force pushes |
| Code Review | __ | <24hr review turnaround, constructive culture, rotating reviewers |
| TDD | __ | 80%+ code coverage, tests written before code, red-green-refactor |
| CI/CD | __ | Automated pipeline, <15 min build, feature flags, canary deploys |
| Architecture | __ | Clear service boundaries, API contracts, documented ADRs |
| API Design | __ | Versioned, documented (OpenAPI), sandbox environment |
| Documentation | __ | ADRs, runbooks, up-to-date READMEs, docs in repo |
| Security | __ | Shift-left, automated SAST/DAST, secrets management |
| Performance | __ | APM in production, load testing, caching strategy, budgets |
| Agile Process | __ | Regular retros, prioritized backlog, clear Definition of Done |
Scoring: 10-20 = Foundation needed | 21-35 = Growing maturity | 36-45 = High performing | 46-50 = Elite team (top 10% per DORA metrics)
1. Version Control and Git Workflows
Version control systems (VCS) like Git are the bedrock of modern software development, providing a systematic way to track changes to code and collaborate effectively. They act as a comprehensive project history, allowing teams to review modifications, revert to previous states, and manage different development lines simultaneously. This practice is fundamental to maintaining order in complex projects and is one of the most critical software development best practices for any team.
Why It's a Best Practice
Effective version control minimizes conflicts, prevents lost work, and provides a safety net for experimentation. A well-defined Git workflow, such as GitFlow or trunk-based development, standardizes how features, bug fixes, and releases are managed. This structure is essential for companies like Google and Microsoft, which manage massive codebases with thousands of daily commits.
How to Implement It
- Choose a Workflow: Decide between GitFlow (ideal for projects with scheduled releases) and trunk-based development (better for CI/CD and rapid iteration). Document the choice and train the team.
- Write Descriptive Commit Messages: Adopt the Conventional Commits specification. A good message (
feat: add user authentication endpoint) is far more useful than a vague one (updated files). - Keep Branches Short-Lived: Encourage developers to create small, focused branches for individual tasks. This reduces merge conflicts and makes code reviews easier. You can use project management tools to link branches directly to tasks, and you can explore more about enhancing team workflows with project management software.
- Enforce Code Reviews: Use pull requests as a gatekeeping mechanism. Require at least one peer review before any code is merged into the main branch.
2. Code Review and Peer Programming
Code review is a systematic process where developers examine each other's code for bugs, logic errors, and adherence to style guidelines before it is merged into the main codebase. It serves as a critical quality gate, while peer programming takes collaboration a step further by having two developers work together on the same task in real-time.
Why It's a Best Practice
At its core, code review is about more than just finding mistakes; it's a powerful mechanism for knowledge sharing and mentorship. When developers review each other's work, junior engineers learn from senior expertise, and senior developers gain new perspectives. Companies like Google have famously documented their rigorous internal review processes, demonstrating how it helps maintain one of the largest and most complex codebases in the world.
How to Implement It
- Keep Pull Requests Small: Aim for PRs that are focused on a single task and between 200-400 lines of code. Research from a 2023 Google study confirms that smaller, faster reviews lead to higher-quality feedback.
- Establish Clear Guidelines: Create a documented checklist covering coding style, architectural principles, and testing requirements.
- Foster a Constructive Culture: Frame feedback as suggestions or questions rather than demands. You can learn more about how to give effective feedback by exploring guides on how to write a peer review.
- Set Time Expectations: Define a reasonable turnaround time for reviews, such as 24 hours, to prevent reviews from becoming a bottleneck.
3. Test-Driven Development (TDD)
Test-Driven Development flips the conventional programming model on its head. Instead of writing code and then testing it, TDD requires developers to write a failing automated test before writing any production code. This "red-green-refactor" cycle ensures that every piece of functionality is directly tied to a specific requirement.
Why It's a Best Practice
TDD forces a focus on requirements before implementation, resulting in cleaner, more modular code design. It naturally leads to comprehensive test coverage, acting as a safety net that catches regressions and provides living documentation. This methodology is crucial for systems where reliability is non-negotiable, such as software used by NASA for space missions, and is heavily encouraged in frameworks like Ruby on Rails and Django.
How to Implement It
- Follow the "Red-Green-Refactor" Cycle: Write a failing test (Red), write the minimum code to pass (Green), then improve the code's structure (Refactor).
- Start with Core Business Logic: Apply TDD to the most critical parts of your application, authentication, payment processing, core algorithms.
- Use Mocks and Fixtures: Isolate the unit being tested by simulating external dependencies like databases or APIs.
- Integrate into CI/CD: Automate test suite execution on every commit for immediate feedback.
4. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
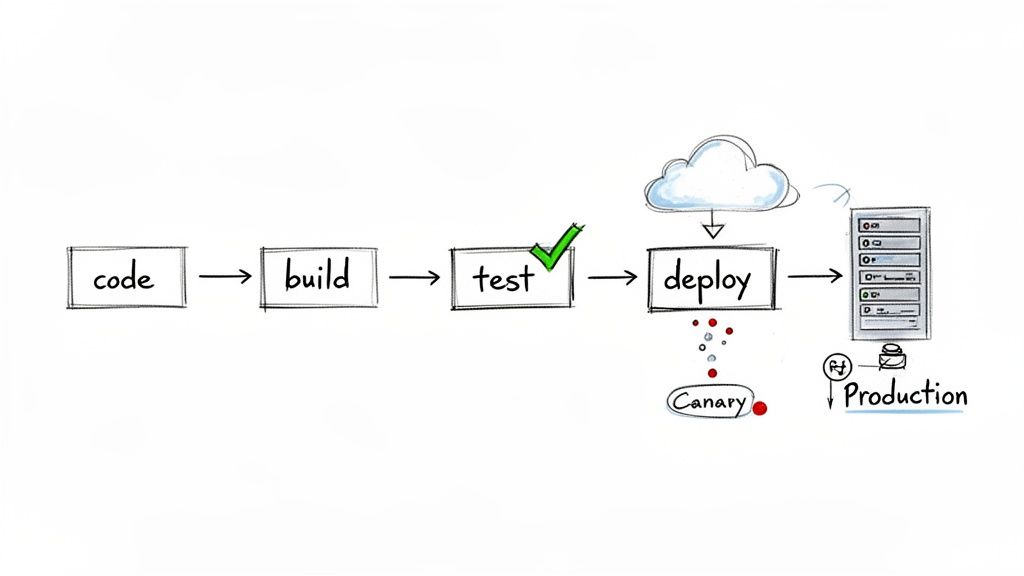
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) automate the software release process from code commit to production. CI automatically builds and tests code changes, ensuring new code integrates smoothly. CD extends this by automatically deploying every validated change.
Why It's a Best Practice
A robust CI/CD pipeline significantly reduces manual errors, shortens feedback loops, and increases development velocity. Netflix famously deploys code thousands of times a day using this approach. The DORA State of DevOps Report consistently shows that elite performing teams deploy 208x more frequently than low performers, and CI/CD is the enabling practice.
How to Implement It
- Start with Continuous Integration: Use tools like GitHub Actions or GitLab CI to run linting, unit tests, and integration tests on every commit.
- Automate All Quality Gates: Integrate automated security scanning (SAST/DAST), performance testing, and code analysis into the pipeline.
- Use Deployment Strategies: Implement canary deployments or blue-green deployments to minimize the blast radius of potential issues.
- Implement Feature Flags: Decouple code deployment from feature release. For those looking to accelerate this setup, explore boilerplate solutions that help you ship your projects faster.
- Monitor and Rollback: Ensure real-time monitoring and a well-tested, one-click rollback procedure.
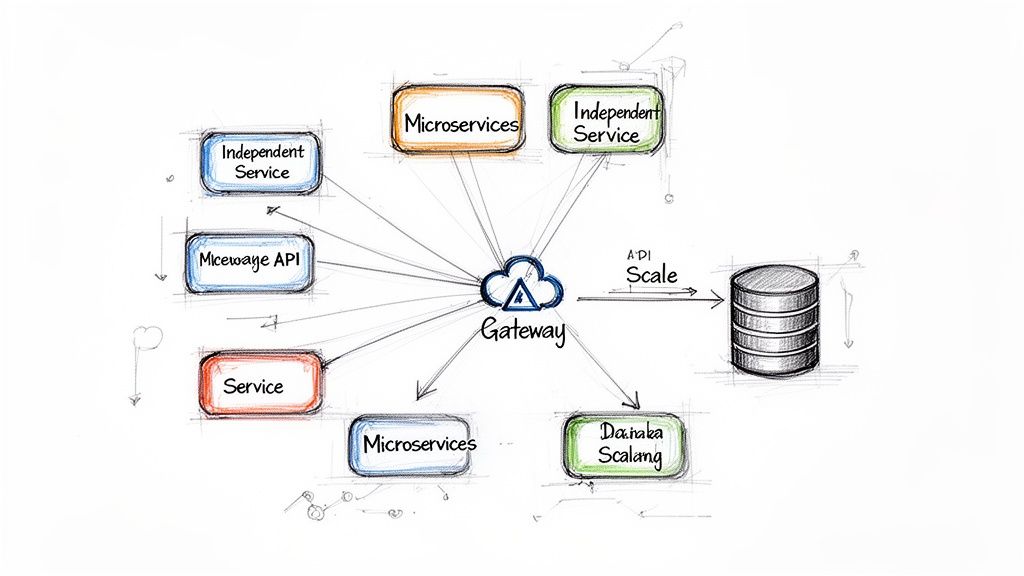
5. Microservices Architecture
Microservices architecture structures an application as a collection of small, autonomous services. Each service is self-contained, organized around a specific business capability, and can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
Why It's a Best Practice
Microservices promote agility and resilience. Since services are decoupled, teams can work on different parts simultaneously without impeding each other. Netflix and Amazon famously transitioned from monoliths to microservices to scale their operations, enabling rapid innovation and fault tolerance.
How to Implement It
- Define Clear Service Boundaries: Start with a well-structured monolith and strategically extract services when clear domains emerge.
- Establish API Contracts: Use standards like OpenAPI (Swagger) to document service contracts.
- Use Containerization and Orchestration: Package each service with Docker and use Kubernetes for automated deployment and scaling.
- Implement Robust Observability: Deploy centralized logging (ELK Stack), distributed tracing (Jaeger), and comprehensive metrics (Prometheus).
6. API Design and Documentation
In a connected digital ecosystem, APIs are the essential connective tissue allowing disparate systems, third-party services, and mobile applications to communicate and share data seamlessly. A well-designed and documented API is a product in itself.
Why It's a Best Practice
Thoughtful API design reduces the learning curve for developers, minimizes integration errors, and fosters a healthy developer community. Companies like Stripe and Twilio built their empires on developer-friendly APIs that are predictable, consistent, and exceptionally well-documented.
How to Implement It
- Choose a Paradigm and Stick to It: Decide whether REST, GraphQL, or gRPC best fits your use case and apply its principles consistently.
- Version Your API from Day One: Introduce versioning in the URL path (e.g.,
/api/v1/users) from the start. - Provide Comprehensive Documentation: Use tools like OpenAPI (Swagger) or Postman to generate interactive documentation.
- Offer a Sandbox Environment: Give developers a safe, isolated environment for testing integrations.
7. Code Documentation and Knowledge Management
Effective documentation ensures that critical project knowledge is accessible and preserved, rather than siloed in individual developers' minds. This includes inline comments, README files, comprehensive wikis, and architecture decision records (ADRs).
Why It's a Best Practice
Comprehensive documentation accelerates onboarding, simplifies maintenance, and reduces the risk of knowledge loss when team members leave. For large-scale open-source projects like Django or enterprise systems at AWS, world-class documentation is non-negotiable.
How to Implement It
- Document the 'Why,' Not Just the 'What': Comments should explain why a particular approach was chosen.
- Use Architecture Decision Records (ADRs): Version-controlled documents recording the context, decision, and consequences of architectural choices.
- Maintain Actionable README Files: Include setup instructions, build commands, and architecture overview.
- Create Runbooks for Operations: Document standard operational tasks in step-by-step guides.
- Version Documentation with Code: Store key documentation in the same Git repository. Enhance with tools that create visual guides, and explore more about creating interactive how-to guides.
8. Security Best Practices and Secure Coding
Integrating security from the very beginning, "Shift Left", is no longer optional. It must be a continuous concern embedded into every development phase, not a final pre-launch check.
Why It's a Best Practice
An "add-on" approach to security is expensive and often too late. Microsoft's Security Development Lifecycle (SDL) has proven that this methodology significantly reduces the risk of costly breaches. According to IBM, fixing a security flaw in production costs 6x more than fixing it during design.
How to Implement It
- Follow Secure Coding Principles: Adhere to the OWASP Top 10. Implement input validation, parameterized queries, and proper CORS/CSP headers. Review comprehensive guidelines on 10 Actionable Software Security Best Practices.
- Manage Dependencies: Use Snyk or Dependabot to scan for known vulnerabilities. Snyk's 2024 report found that 80% of vulnerabilities are in transitive dependencies.
- Protect Secrets and Credentials: Never hardcode secrets. Use HashiCorp Vault or AWS Secrets Manager.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Implement automated SAST/DAST in your CI/CD pipeline. Supplement with periodic penetration testing. Leverage tools like CyberUpgrade to streamline audits.
9. Performance Optimization and Monitoring
Performance optimization ensures applications are efficient, responsive, and scalable. It involves systematically identifying and eliminating bottlenecks to improve speed and resource consumption.
Why It's a Best Practice
For businesses like Amazon, even a 100-millisecond delay in page load time causes a 1% drop in sales. Google found that 53% of mobile users abandon sites taking longer than 3 seconds to load. Proactive performance monitoring provides the visibility to detect issues before they affect users.
How to Implement It
- Implement APM: Use Datadog, New Relic, or Prometheus to track transaction times, error rates, and resource utilization.
- Establish a Caching Strategy: Implement caching at CDN, application (Redis), and database levels.
- Optimize Database Queries: Ensure proper indexing, rewrite inefficient queries, and use connection pooling.
- Profile Your Code: Use profilers to identify inefficient functions consuming excessive CPU or memory.
- Conduct Load Testing: Use k6 or JMeter to simulate traffic and identify performance limits before releases.
10. Agile Development and Iterative Delivery
Agile methodologies have replaced rigid waterfall approaches by emphasizing iterative progress, continuous feedback, and adaptive planning. Frameworks like Scrum and Kanban enable teams to respond quickly to changing requirements and deliver value incrementally.
Why It's a Best Practice
Adopting an Agile mindset allows teams to build, test, and release software faster. Tech giants like Spotify (squad-based model) and Amazon ("two-pizza team" rule) have used Agile principles to innovate at scale. The 17th State of Agile Report (2023) highlights that the top benefits are enhanced ability to manage changing priorities and accelerated software delivery.
How to Implement It
- Adopt a Framework: Choose Scrum for defined sprints or Kanban for continuous flow.
- Maintain a Prioritized Backlog: Keep a single, ordered list with the most valuable items at the top.
- Conduct Regular Ceremonies: Daily stand-ups (15 minutes max), sprint planning, and retrospectives.
- Focus on Working Software: Deliver a functional increment at the end of each iteration with a clear "Definition of Done."
- Utilize Agile Tools: Leverage Jira, Linear, or GitHub Projects to visualize workflows and track progress.
"Any organization that designs a system will produce a design whose structure is a copy of the organization's communication structure. If you want better software architecture, you need better team architecture first."
-- Melvin Conway (Conway's Law), referenced by Martin Fowler, ThoughtWorks Chief Scientist
10-Point Comparison of Software Development Best Practices
| Practice | Implementation Complexity | Resource Requirements | Expected Outcomes | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version Control | Low-Medium | Low | Traceability, safe rollbacks | Multi-team codebases |
| Code Review | Medium | Low-Medium | Fewer bugs, shared knowledge | Code merges, onboarding |
| TDD | Medium-High | Medium | Fewer regressions, easier refactoring | Core business logic, libraries |
| CI/CD | High | High | Faster, safer deployments | Frequent releases, high-velocity teams |
| Microservices | Very High | High | Independent scaling, fault isolation | Large modular products |
| API Design | Medium | Low-Medium | Easier integrations, decoupling | Third-party integrations, mobile clients |
| Documentation | Low-Medium | Low | Faster onboarding, less knowledge loss | Scaling teams, complex systems |
| Security | Medium-High | Medium-High | Reduced breach risk, compliance | Services handling user data |
| Performance | Medium-High | Medium | Better UX, cost savings | High-traffic services |
| Agile | Medium | Low-Medium | Faster time-to-market | Evolving product requirements |
Using AI to Accelerate Software Development Best Practices
AI-powered development tools have matured significantly in 2026. Here are specific ways to use AI assistants like ChatGPT, Claude, and GitHub Copilot to implement the best practices covered in this guide:
Prompt: Architecture Decision Record Generation
"Write an Architecture Decision Record (ADR) for the decision to [migrate from monolith to microservices / adopt PostgreSQL over MongoDB / implement event-driven architecture]. Include: Context, Decision, Consequences (positive and negative), and Alternatives Considered. Format as Markdown."
Prompt: Test Case Generation
"Given this [function/API endpoint], write comprehensive unit tests following TDD principles. Include: happy path, edge cases, error handling, and boundary conditions. Use [Jest/pytest/JUnit] with clear test descriptions following the 'Given-When-Then' pattern."
Prompt: Security Code Review
"Review this code for security vulnerabilities against the OWASP Top 10. Check for: SQL injection, XSS, insecure deserialization, hardcoded secrets, improper error handling, and missing input validation. Provide specific line-by-line recommendations with code fixes."
Prompt: CI/CD Pipeline Configuration
"Create a GitHub Actions CI/CD pipeline for a [Node.js/Python/Java] application that includes: linting, unit tests, integration tests, SAST scanning with Snyk, Docker image building, and deployment to [AWS ECS/Kubernetes] with a canary deployment strategy. Include caching for dependencies."
Prompt: Performance Optimization Analysis
"Analyze this [database query / API endpoint / React component] for performance bottlenecks. Suggest optimizations including: caching strategies, query optimization (with EXPLAIN plan analysis), lazy loading, pagination, and connection pooling. Estimate the expected performance improvement for each suggestion."
Common Mistakes That Derail Development Teams
5 Development Anti-Patterns to Eliminate
- Skipping code reviews to "move faster." Teams that skip reviews deploy 33% more bugs to production (SmartBear State of Code Review). The time "saved" is immediately consumed by debugging, hotfixes, and customer escalations. Google's engineering team found that code reviews catch 15% of bugs that automated tests miss.
- Writing tests after the feature is "done." When tests are treated as an afterthought, coverage drops to 20-30% and tests are shallow. TDD practitioners achieve 80-90% coverage naturally because every line of production code has a corresponding test. The difference shows up during refactoring: TDD codebases have 40-80% fewer defects per KLOC (IBM Research).
- Premature microservices adoption. Startups with 2-5 developers should not start with microservices. The operational overhead of managing distributed systems, service discovery, and network failures outweighs any modularity benefit at small scale. Martin Fowler's advice: "Don't start with microservices, start with a well-structured monolith."
- Treating documentation as "we'll do it later." "Later" never comes. The cost of documentation grows exponentially the longer you wait, a function documented at creation takes 10 minutes; the same function documented 6 months later takes 2-3 hours of code archaeology. Embed documentation in the Definition of Done for every sprint.
- Deploying without a rollback plan. According to DORA metrics, elite teams recover from failures in less than 1 hour. Teams without rollback procedures average 1 week. Every deployment should have a tested rollback path. Practice it regularly, a rollback you've never tested is a rollback that won't work.
From Principles to Practice: Embracing a Culture of Excellence
This guide has journeyed through ten foundational software development best practices, moving from the granular details of Git workflows and Test-Driven Development (TDD) to the high-level strategies of microservices architecture and agile delivery. Each practice represents more than just a technical task; it's a strategic investment in the long-term health and success of your projects.
The true power of these concepts is unlocked when they are not treated as isolated checklist items but woven together into a cohesive development culture. A well-documented API is exponentially more valuable when supported by a robust CI/CD pipeline that tests it automatically. A secure coding mindset is amplified when combined with regular peer reviews that catch vulnerabilities early. This interconnectedness creates a flywheel effect: quality begets speed, and reliability fosters innovation.
The Shift from Rules to Habits
The ultimate goal is to transition these principles from rigid rules into ingrained team habits. Initially, implementing TDD or a strict Git branching strategy might feel cumbersome. However, as teams gain fluency, these practices become second nature, reducing cognitive overhead and allowing developers to focus on solving complex business problems.
Your Actionable Path Forward
Don't attempt to implement all ten practices at once. Instead, identify your most significant pain point and start there:
- Deployment is a manual nightmare? Focus on implementing a basic CI/CD pipeline with GitHub Actions or GitLab CI.
- Codebase is difficult for new hires? Prioritize code documentation and establish a knowledge management hub.
- Bugs frequently discovered by users? Introduce a more formal code review process or experiment with pair programming.
Select one area, build momentum, and expand. The key is continuous improvement, not instantaneous perfection. For teams looking to upskill in emerging areas, practical training from institutions like the Techpresso AI Academy can provide a crucial competitive edge.
Ultimately, mastering these software development best practices is about building better products, fostering more effective teams, and creating a sustainable, resilient engineering culture. It's a commitment to craftsmanship that pays dividends in reliability, scalability, and user satisfaction.
Is your team struggling to manage multiple staging, review, and development environments? Dupple automates the creation of on-demand, full-stack preview environments for every pull request, directly integrating with your CI/CD workflow. Visit Dupple to see how you can ship with greater confidence and speed.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most important software development best practices for startups?
For startups, focus on three fundamentals: version control with a clear branching strategy (trunk-based development for speed), CI/CD automation (even a basic pipeline saves 20+ hours/month), and code reviews (catch bugs before users do). Skip microservices initially, a well-structured monolith is faster to develop and deploy. Add TDD and formal documentation as the team grows past 5-8 developers.
How do you measure the impact of development best practices?
Use the four DORA (DevOps Research and Assessment) metrics: deployment frequency, lead time for changes, change failure rate, and time to restore service. Elite teams deploy multiple times per day with less than 15% change failure rate and less than 1 hour recovery time. Track these metrics monthly using tools like Sleuth, LinearB, or Haystack to quantify improvement.
What is the biggest mistake teams make with software development practices?
Trying to implement everything at once. Teams that attempt to adopt TDD, microservices, and full CI/CD simultaneously experience "practice fatigue" and revert to old habits within 3 months (ThoughtWorks Technology Radar). Instead, adopt one practice per quarter, let it become habitual, then add the next. The compounding effect of sequential adoption far exceeds the impact of simultaneous but shallow implementation.
How does AI change software development best practices?
AI tools like GitHub Copilot, Claude, and ChatGPT accelerate implementation but don't replace fundamentals. Copilot-generated code still needs code review, studies show it introduces subtle bugs in 40% of suggestions (Stanford/NYU research). AI excels at: generating test cases, writing documentation, creating boilerplate CI/CD configs, and identifying security vulnerabilities. The best practice is to use AI as an accelerator for human developers, not a replacement for process discipline.






