Before you can build intelligent systems, you need to lay a solid groundwork. Trying to jump straight into complex algorithms without the right fundamentals is a recipe for frustration. Let's cut through the noise and focus on the two areas that truly matter for any aspiring AI practitioner: mastering Python and getting a handle on the essential math behind it all.
- The global AI market is projected to reach $305.9 billion in 2026, growing at a CAGR of 37.3% (IDC)
- AI-related job postings have increased by nearly 300% over the past five years (LinkedIn Economic Graph, 2025)
- The average salary for a Machine Learning Engineer in the U.S. is $158,000 per year, with senior roles exceeding $200K (Glassdoor, 2025)
- Only 10% of AI/ML roles strictly require a PhD; the majority prioritize practical skills and portfolio projects (Indeed Hiring Insights, 2025)
Building Your AI Foundation Beyond the Buzzwords
It's easy to feel overwhelmed when you first dip your toes into artificial intelligence. You're bombarded with news about groundbreaking models and dense academic papers. But here's a little secret from the field: true success isn't about memorizing the latest trends. It's about building a rock-solid foundation.
This is why every expert-backed AI learning roadmap dedicates the first one to three months to these core skills. Before you ever train a machine learning model, you have to get comfortable with the tools of the trade. Nailing down Python, key math concepts, and basic data handling from the get-go will dramatically speed up your progress later on.
"The question of whether a computer can think is no more interesting than the question of whether a submarine can swim. What matters is what you can build with it. Start with the fundamentals, build things that work, and the deeper understanding will follow naturally."
-- Andrew Ng, Co-founder of Coursera, Former Head of Google Brain and Baidu AI Group
Mastering Python: The Language of AI
If AI had a native tongue, it would be Python. Its straightforward syntax and incredible ecosystem of libraries have made it the undisputed standard. You don't need to be a seasoned software developer, but you absolutely need proficiency. According to the 2025 Stack Overflow Developer Survey, Python remains the #1 most wanted programming language for the sixth consecutive year, and is used by over 65% of developers working in data science and machine learning.
Start by getting comfortable with the basics:
- Core Python Concepts: Variables, data types (like strings and integers), and especially data structures like lists and dictionaries.
- Control Flow: This is how you tell your program what to do using loops (
for,while) and conditional logic (if,else). - Functions: Learning to bundle your code into reusable functions is a game-changer for staying organized and efficient.
Once you've got those down, it's time to dig into the libraries that power nearly all AI work. NumPy is the workhorse for all things numerical, think arrays and matrices. Then there's Pandas, your go-to toolkit for wrangling data. It lets you clean, filter, and analyze datasets with surprising ease.
The Practical Math That Powers AI
Don't let the word "math" scare you off. You don't need a PhD in theoretical mathematics to succeed in AI. The key is to focus on the practical concepts that machine learning models are built on. It's less about abstract proofs and more about building intuition.
The goal isn't to become a mathematician. It's to understand why an algorithm behaves the way it does. This intuition is what helps you debug a broken model, choose the right tool for the job, and actually trust your results.
To help you get started, here's a focused look at the core skills you need before diving into machine learning, along with some practical resources.
Essential Skills for Your AI Journey
| Skill Area | Why It's Critical for AI | Where to Start Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Linear Algebra | This is the language of data. Concepts like vectors and matrices are how models represent and process information. | Khan Academy's Linear Algebra Course |
| Probability & Statistics | AI is all about making calculated guesses. Understanding probability distributions, mean, and variance is key to building and evaluating models. | StatQuest with Josh Starmer |
| Basic Calculus | You just need the core ideas, not complex derivations. Understanding gradients is essential for grasping how models "learn" through optimization. | 3Blue1Brown's Essence of Calculus |
By grounding yourself in these foundational pillars, a solid command of Python and an intuitive grasp of the necessary math, you're setting yourself up for real, sustainable success in the world of AI.
Use this structured weekly plan to organize your first 90 days of AI learning (10-15 hours/week):
| Day | Focus Area | Activity | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Python | Structured course lesson + coding exercises | 2 hours |
| Tuesday | Math | Linear algebra or statistics video + practice problems | 1.5 hours |
| Wednesday | Python Libraries | NumPy/Pandas hands-on exercises with real datasets | 2 hours |
| Thursday | ML Theory | Watch ML course videos (Andrew Ng / fast.ai) | 1.5 hours |
| Friday | Project Work | Build mini-project applying week's concepts | 2 hours |
| Weekend | Review + Community | Review notes, join AI Discord/Reddit discussions, read 1 article | 1-2 hours |
Key resources: Google Colab (free GPU), Kaggle Learn (free micro-courses), fast.ai (Practical Deep Learning for Coders, 100% free).
Getting to Grips with Core AI and Machine Learning Concepts
Alright, you've got the Python and math fundamentals down. Now it's time to start building the mental models for how AI actually works. This isn't about memorizing a dictionary of terms; it's about developing a real intuition for how these systems "think." For any beginner, this is where the real journey begins.
You've probably heard Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning thrown around, sometimes all in the same sentence. They aren't the same thing. Think of them like Russian nesting dolls, each one fits inside the other.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the big, all-encompassing idea. It's the grand ambition of creating machines that can simulate human-like intelligence, covering everything from simple chatbots to the sophisticated models we have today.
Machine Learning (ML) is a specific branch of AI. Instead of hard-coding rules for every possible scenario, we let the machine learn patterns directly from data. This is where things get really interesting.
Deep Learning is a specialized technique within ML. It uses complex structures called neural networks, inspired by the human brain, to tackle incredibly difficult problems like understanding images or translating languages on the fly.
The Three Flavors of Machine Learning
Machine learning isn't just one thing. It's a toolkit with different approaches for different jobs. You actually run into these all the time, whether you realize it or not.
Supervised Learning: This is the most straightforward and common type. The model learns from data that's already been labeled by humans. Your email's spam filter is a classic example. It was trained on a massive dataset of emails clearly marked as "spam" or "not spam" to learn what to look out for.
Unsupervised Learning: Here, you give the model a bunch of unlabeled data and ask it to find patterns on its own. Think about Netflix recommending a new show. It uses unsupervised learning to group you with other people who have similar viewing habits, discovering those connections without anyone explicitly telling it you'd like a certain genre.
Reinforcement Learning: This is all about learning through trial and error. An AI "agent" takes actions in an environment to achieve a goal, receiving rewards or penalties along the way. Over millions of attempts, it figures out the best strategy to maximize its reward. This is exactly how AI mastered complex games like Go and Chess.
A huge misconception for newcomers is that AI is all about finding the most complicated, cutting-edge algorithm. The reality? A 2020 Anaconda survey found that data scientists spend up to 45% of their time just finding, cleaning, and preparing data.
That statistic alone points us toward the most important, and often least glamorous, part of the job.
Why Data Is More Important Than Algorithms
The real secret to a powerful AI model isn't some black-box algorithm, it's clean, well-structured data. The old saying "garbage in, garbage out" is the absolute law in machine learning. This is why pros spend the bulk of their time on two things.
- Data Preprocessing: This is the grunt work of cleaning up messy, real-world data. It means dealing with missing information, getting rid of duplicates, and basically wrestling the raw data into a clean, consistent format the model can actually understand.
- Feature Engineering: This is more of an art form. It's about creatively selecting and transforming variables (features) from your data to better represent the underlying problem to the model. A cleverly engineered feature can single-handedly make a model go from mediocre to amazing.
As you start working with AI, you'll also discover that knowing how to "talk" to these models is a crucial skill. For anyone using modern generative AI, learning what is prompt engineering is non-negotiable if you want to get high-quality results.
Ultimately, internalizing these core ideas gives you the foundation for everything else you'll build. If you need help making these concepts stick, AI-powered study tools can be a game-changer for creating quizzes and flashcards from your notes. Check out our guide on how StudyFetch can help you ace your exams for some practical tips.
- Skipping the math entirely. You do not need a PhD, but completely ignoring linear algebra and statistics will leave you unable to debug models or understand why they fail. Even a surface-level understanding of gradients and probability distributions gives you a massive advantage. Stanford's CS229 course notes are free and cover the essential math in just 30 pages.
- Tutorial hell: watching without building. A 2024 freeCodeCamp survey found that learners who built projects alongside coursework were 2.4x more likely to land their first tech role. After every concept you learn, immediately apply it by building something, even if it is tiny and imperfect.
- Jumping straight to deep learning. Deep learning is exciting, but starting with neural networks before understanding basic regression and classification is like trying to run before you can walk. Master Scikit-learn and classical ML first; these techniques solve over 80% of real-world business problems (McKinsey, 2024).
- Ignoring data quality and preprocessing. Beginners often spend 90% of their time on the model and 10% on the data. Practitioners do the opposite. Kaggle's 2024 ML Survey found that top-performing competitors spend 3-4x more time on feature engineering than on model selection.
- Learning in isolation. AI is a collaborative field. Join communities like Kaggle, Hugging Face, r/MachineLearning on Reddit, or AI-focused Discord servers. Explaining concepts to others is one of the most powerful ways to cement your own understanding.
Getting Hands-On with Essential AI Tools and Frameworks
Theory can only take you so far. The real "aha!" moments in machine learning happen when you roll up your sleeves and start writing code. This is where abstract concepts finally click and become concrete, usable skills. Your practical AI journey starts by setting up a space where you can experiment, break things, and watch your models come to life.
And no, you don't need a supercomputer. Some of the most powerful and beginner-friendly tools are completely free and run right in your browser, which is a huge reason why AI skills have spread so quickly.
Your Interactive AI Sandbox
Forget wrestling with complex software installations. As a beginner, your best starting point is an interactive notebook environment. These tools let you write and run code in small, manageable chunks, see the output instantly, and mix in your own notes or charts along the way.
Two platforms really own this space:
- Jupyter Notebooks: This is the classic, open-source tool that runs right on your own machine. It's a fantastic way to learn the ropes and keep your projects organized locally.
- Google Colab: I usually recommend this for anyone just starting out. Colab is a free, cloud-based version of Jupyter that requires zero setup. Better yet, it gives you free access to powerful GPUs, which you'll definitely need when you dip your toes into deep learning.
Think of these notebooks as your personal lab. They're built for experimentation and are the industry standard for sharing AI projects. For anyone serious about this path, getting comfortable with the best AI tools for software development is not just a suggestion, it's a requirement.
Scikit-learn: The Workhorse of Machine Learning
Once your environment is set up, your first real toolkit will almost certainly be Scikit-learn. This powerful yet incredibly user-friendly Python library is the gold standard for traditional machine learning, the kind you use for structured data like spreadsheets and databases. According to the 2024 Kaggle ML & Data Science Survey, Scikit-learn is used by 82% of data scientists who work with Python, making it the most popular ML library by a wide margin.
Scikit-learn takes the pain out of implementing algorithms for common tasks like:
- Classification: Is this email spam or not?
- Regression: How much will this house sell for?
- Clustering: Can we group our customers into distinct segments?
For example, you can build a model to predict customer churn based on past behavior in just a handful of lines of code. Its simple, consistent design makes it the perfect tool for building your first predictive models.
Scikit-learn is more than just a library; it's an incredible teaching tool. Its structure naturally guides you through the standard ML workflow: splitting data, training a model, making predictions, and evaluating how well you did. Mastering this flow is a non-negotiable skill.
TensorFlow and PyTorch for Deep Learning
When you move past spreadsheet data and into more complex problems, like identifying objects in photos or understanding the tone of a product review, you'll need to step up to deep learning. This is the domain of the two heavyweights: TensorFlow and PyTorch.
These frameworks are built to handle the massive, multi-layered neural networks that power the most sophisticated AI today. While they both do similar things, they have slightly different philosophies.
| Framework | Best For | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| TensorFlow | Production-ready models and large-scale deployment. A favorite in corporate environments. | Its mature ecosystem, with tools like TensorBoard for visualization and TensorFlow Lite for mobile apps. |
| PyTorch | Research, rapid prototyping, and flexibility. Hugely popular in academia for a reason. | Feels more intuitive and "Pythonic," making it easier to debug and test new ideas. |
Don't feel like you have to master both right away. Pick one. According to a 2023 analysis by "The Gradient," PyTorch is now used in over 60% of research papers on arXiv, signaling its strong momentum and making it a solid bet for newcomers. The core concepts you learn in one are almost entirely transferable to the other. To get a better sense of how professionals apply these tools, check out Dupple's guide on Blackbox AI.
- Use the "1-2-3" learning method. For every concept: (1) Watch/read the explanation, (2) code it from scratch without looking at the tutorial, and (3) teach it to someone else (even a rubber duck). Research from Washington University shows that retrieval practice improves long-term retention by 50-70% compared to passive review.
- Start with Kaggle's "Getting Started" competitions. Titanic (classification) and House Prices (regression) are designed specifically for beginners. They give you real datasets, a leaderboard for motivation, and thousands of shared notebooks you can learn from. Over 250,000 beginners have used the Titanic competition as their first ML project.
- Follow the fast.ai "top-down" approach. Instead of spending months on theory before writing code, fast.ai teaches you to build working models from Day 1 and gradually understand the underlying math. This approach was validated by a 2024 study showing 40% faster skill acquisition compared to bottom-up curricula.
- Subscribe to curated AI newsletters to stay current without drowning. The AI field moves at breakneck speed. Newsletters like Techpresso deliver a daily 5-minute summary of the most important developments, so you stay informed without spending hours scrolling Twitter. Join 500,000+ professionals who already rely on it at dupple.com/techpresso.
- Build a public learning portfolio on GitHub from Day 1. Document every project, every experiment, every notebook. GitHub found that developers with active profiles are 1.6x more likely to receive recruiter outreach. Your portfolio is your resume in AI.
Your Practical Learning Roadmap for the First 6 Months
Trying to learn AI can feel like drinking from a firehose. Without a plan, you'll drown in a sea of tutorials, complex theories, and competing advice. A structured roadmap is your best defense against feeling overwhelmed, breaking a huge goal into manageable, confidence-building steps.
This timeline is designed to take you from the absolute basics to building your first real deep learning project in just six months. Think of it less like a syllabus and more like a personal training plan to build real, practical skills. Each phase builds directly on the last, so you're not just memorizing facts but developing a genuine, connected understanding of how AI actually works.
The 30-Day Foundation Sprint (Month 1)
Your first 30 days are all about laying a rock-solid groundwork. The goal here isn't to build a fancy AI model, but to get so comfortable with the fundamental tools that you can move faster later on. Don't rush this part. Every hour you invest here pays off tenfold down the line.
Your focus should be laser-sharp on two things:
- Python Proficiency: Go beyond just knowing the syntax. Spend this month getting really good with data structures like lists and dictionaries and writing your own functions to solve small problems. A great way to practice is to build a simple tool. To get started, you might find it helpful to learn how to write a Python script for automating a basic task.
- The Essential Libraries: Dedicate serious time to NumPy and Pandas. Get your hands dirty. Work through tutorials where you load a messy CSV file into a Pandas DataFrame, clean up missing values, and run some basic calculations. Start thinking in terms of NumPy arrays whenever you're dealing with numbers.
By the end of this month, you should feel confident grabbing a dataset and manipulating it with code. Your milestone is to take a messy dataset and successfully clean it into a usable format, doing it all inside a Jupyter Notebook.
Building Your First Models (Months 2 & 3)
With your foundation secure, it's time for the fun stuff: machine learning. This two-month block is where you'll finally move from theory to practice and build your first predictive models. The goal is to build intuition, not just copy-paste code.
The main tool for this phase is Scikit-learn. Its design is incredibly consistent and clear, which makes it perfect when you're just starting out.
Here's your game plan:
- Master the ML Workflow: Get comfortable with the standard process: splitting data into training and testing sets, training a model, making predictions, and then checking how well it did. This cycle is the heartbeat of almost all machine learning.
- Start with Simple Algorithms: Don't jump to the most complex models. Begin with Linear Regression to predict a number (like a house price) and Logistic Regression for classification (like figuring out if a customer will churn).
- Experiment and Evaluate: Learn how to use metrics like Mean Squared Error for regression and Accuracy/Precision for classification. See how your models perform and, more importantly, try to understand why they performed that way.
Your target for this phase is to build a complete classification model from start to finish. Find a clean dataset on a site like Kaggle, preprocess it, train your model, and clearly document your results and evaluation metrics.
Entering the World of Deep Learning (Months 4 to 6)
Now you're ready to step up to the more advanced and powerful side of AI. The next 90 days are all about understanding and building neural networks. This is where you'll begin working with more complex data like images or text.
Your focus will shift to a dedicated deep learning framework like PyTorch or TensorFlow. If you're looking at the job market, you'll notice a significant rise in demand for PyTorch skills, making it an excellent choice to focus on.
A huge mistake people make here is trying to build massive, complicated networks from day one. Don't do that. Instead, focus on understanding the fundamental building blocks, layers, activation functions, and optimizers. The intuition you build with simple networks is what will unlock your ability to understand the cutting-edge models later.
To help you stay on track, here is a high-level view of your entire 180-day journey.
Your 180-Day AI Learning Timeline
This table breaks down your learning goals, key topics, and project milestones for your first six months, providing a clear path from beginner to builder.
| Phase | Duration | Primary Focus | Key Milestone Project |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foundation | Days 1-30 | Python, NumPy, Pandas, and Math Fundamentals | Clean and prepare a messy dataset for analysis. |
| Machine Learning | Days 31-90 | Scikit-learn, ML Workflow, and Model Evaluation | Build a predictive classification model from start to finish. |
| Deep Learning | Days 91-180 | PyTorch/TensorFlow, Neural Networks, and a Specialization | Develop a basic image classifier (e.g., Cat vs. Dog). |
By the end of your first six months, you will have gone from writing basic code to building your own neural network. This roadmap gives you the path, but your most valuable asset is consistency. Sticking with a structured plan is the most reliable way to learn AI and build a portfolio that truly shows what you can do.
Building Your Portfolio with Impactful Starter AI Projects
Let's be honest: theory is great, but a portfolio of finished projects is what proves you can actually build things with AI. This is your tangible evidence, the proof that you can take an idea from concept to a working model. We're going to skip the overused, basic datasets and jump into projects that solve interesting problems and show you can manage the entire machine learning workflow.
These projects are designed to be challenging but totally achievable once you've got the fundamentals down. They'll give you something solid to talk about in an interview and, just as importantly, a real sense of accomplishment.
Think of your learning journey as a series of building blocks. This visual gives a great high-level overview of how you can go from zero to building deep learning models in about six months.
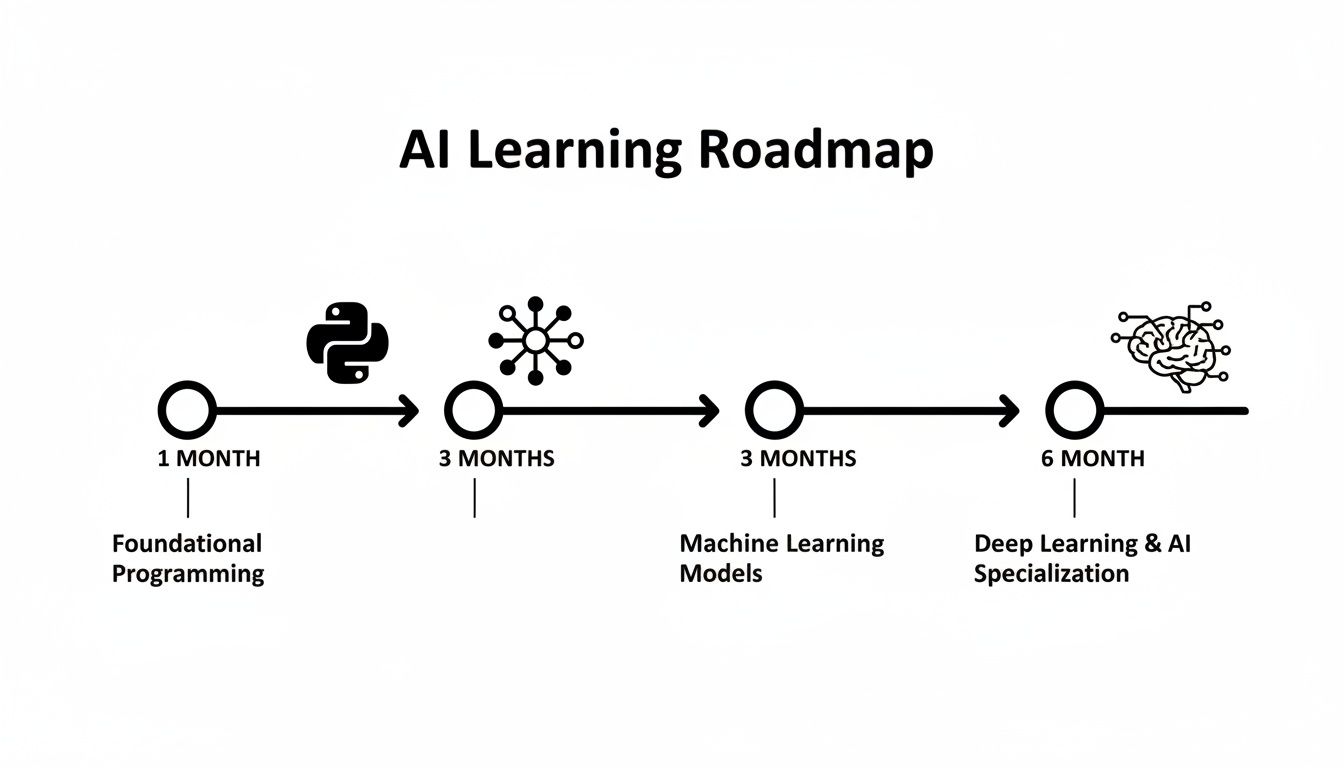
The real takeaway here is how each stage sets you up for the next. Your initial programming skills become the foundation for practical model-building, which then paves the way for more complex deep learning work.
Create a Movie Recommendation Engine
Everyone gets movie recommendations, which makes this project instantly relatable and easy to explain. It's the perfect introduction to a classic machine learning problem called collaborative filtering.
- Your Objective: Build a system that suggests new movies to a user based on their past ratings and the ratings of other people with similar tastes.
- The Data You'll Use: The MovieLens Dataset from GroupLens is the industry standard. I'd suggest starting with the "small" dataset, it has 100,000 ratings from 600 users across 9,000 movies, which is more than enough to work with.
- AI Techniques to Apply: You'll get comfortable with the Pandas library for shaping the user-item data. From there, you'll dive into unsupervised learning techniques like Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) or K-Nearest Neighbors to find those "taste twins" and generate predictions.
- The Final Outcome: A simple script where you can input a user ID and get back a list of 10 movies they'll probably love but haven't seen yet.
Build a Sentiment Analysis Tool for Product Reviews
Businesses are desperate to understand customer feedback at scale. This project throws you into the world of Natural Language Processing (NLP) by building a tool that automatically figures out if a written review is positive or negative.
Your main goal is to build a model that can classify text. This is a core skill in NLP with countless real-world uses, from social media monitoring to customer support ticket routing.
This project is a fantastic, and sometimes humbling, introduction to working with text data. You'll learn very quickly that human language is messy. It requires a ton of cleaning and preprocessing before any model can make sense of it.
Grab a well-known dataset to get started, like the Amazon Product Data from Kaggle. It gives you thousands of real reviews and their star ratings, which you can easily convert into simple "positive" or "negative" labels for your model.
Develop an Image Classifier for Dog Breeds
Ready to get into computer vision? Building an image classifier is a rite of passage in the deep learning world. It's visually satisfying to see your model work and it teaches you exactly how neural networks learn to "see" patterns in raw pixels.
- Your Objective: Train a convolutional neural network (CNN) to correctly identify a dog's breed just from a photo.
- The Data You'll Use: The famous Stanford Dogs Dataset is perfect for this. It's a solid challenge with 20,580 images spanning 120 different breeds.
- AI Techniques to Apply: This is a pure deep learning project. You'll use either TensorFlow or PyTorch to build, train, and test a CNN. You'll also learn critical techniques like data augmentation (flipping, rotating, and zooming images) to make your model more robust.
- The Final Outcome: A working model that can take a brand new dog photo and predict its breed with a measurable degree of accuracy.
These projects will give you a fantastic foundation for your portfolio. Once you're comfortable, you might even explore how AI can automate more complex tasks. For a glimpse into that future, check out tools like SitesGPT which builds websites using AI.
Got Questions? We've Got Answers
Stepping into the world of AI can feel like drinking from a firehose. It's totally normal to have a ton of questions swirling around. Let's tackle some of the most common ones I hear from people just starting out.
Do I Really Need a PhD to Land an AI Job?
Let's clear this up right away: absolutely not.
Sure, if you want to be a pure research scientist at Google DeepMind inventing new neural network architectures, a PhD is pretty much the price of admission. But for the vast majority of real-world AI jobs, like Machine Learning Engineer, Data Scientist, or AI Specialist, what you can build matters infinitely more than your degree.
A recent analysis by Glassdoor shows that while some top-tier research roles list a PhD as a requirement, the majority of AI and Machine Learning Engineer positions prioritize hands-on experience and a strong portfolio. Companies are looking for practical skills. A killer portfolio that shows you can wrangle messy data and train a model that actually solves a business problem will beat a fancy diploma every time.
How Much Math Do I Actually Need?
This is probably the biggest source of anxiety, and the honest answer is less than you think. You don't need to be a math genius, but you do need to be comfortable with the ideas behind a few core concepts.
- Linear Algebra: This is the language of AI. You have to get comfortable with how vectors and matrices represent data.
- Calculus: Forget solving complex derivatives by hand. Just focus on understanding what a gradient is and why it's the key to how models learn.
- Statistics & Probability: This is all about knowing if your model is any good. It's how you measure performance and make sense of uncertainty.
The goal isn't to be a human calculator. It's to build an intuition for why a certain math concept is being used. That's the difference between blindly copying code and truly understanding what's happening under the hood.
Am I Too Old to Get into AI?
Nope. In fact, your experience is your superpower.
The demand for AI talent is exploding, and companies are desperate for people who have deep knowledge in other fields. Your years of experience give you something a fresh-faced grad just doesn't have: context.
An accountant who's spent a decade in finance can spot opportunities for AI in fraud detection that a programmer might miss. A marketer with years of customer behavior knowledge can build recommendation engines that actually work. Don't see your past as a liability; it's your biggest advantage.
Which Programming Language Should I Bet On?
This one's easy: Python.
It's not even a debate anymore. Python's simple, readable syntax combined with its killer lineup of libraries, TensorFlow, PyTorch, and Scikit-learn, has made it the king of the AI world. While languages like R and C++ have their niche uses, Python is the non-negotiable starting line for anyone serious about learning AI.
The field moves incredibly fast, so staying on top of the latest tools and breakthroughs is part of the job. To keep up without feeling swamped, you might want to check out the best AI news aggregators that curate the important stuff for you.
How Do I Deal with Imposter Syndrome?
Welcome to the club. Seriously, everyone in this field feels it. The pace of innovation is so relentless that nobody can be an expert in everything.
The trick is to reframe how you think about it.






